Poll 08-19: Reference Variables and Unix¶
Unix File Hierarchy
Note
This question tests the students’ ability to understand the Unix
File Hierarchy using sample output from the tree command.
The exercise is very similar to the book question in section
2.7 - Additional Practice.
Question 1
Suppose that you are working directly inside of your home
directory on Odin, execute the tree command, and observe the
output below:
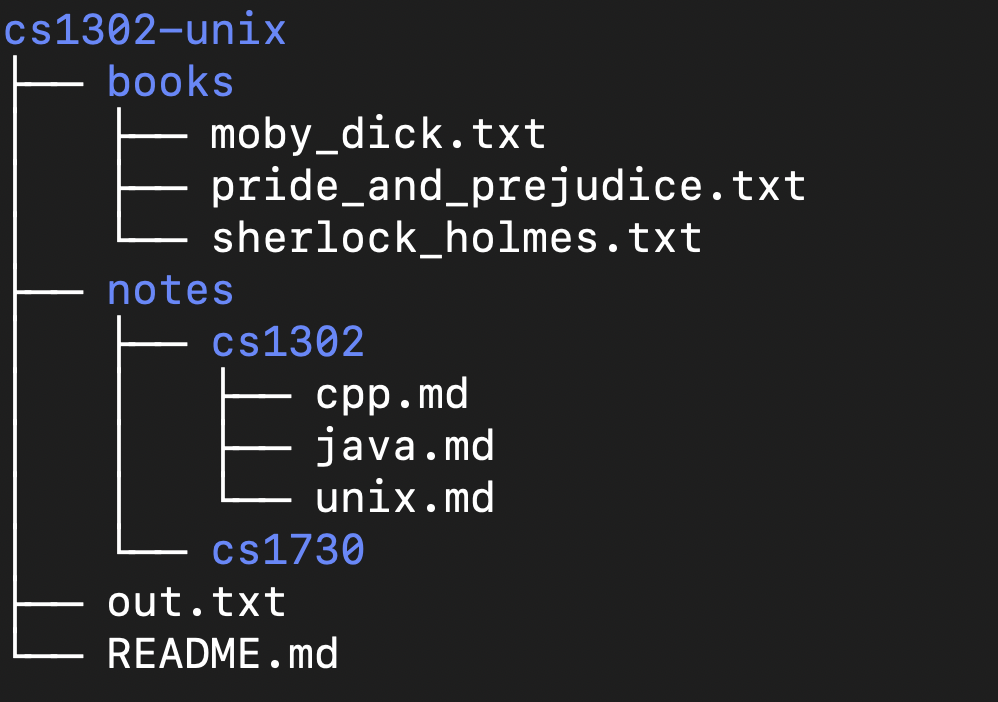
If /home/users/user is the absolute path to your present
working directory (also your home directory), then which of the
commands shown below would move you directly into the 1302
directory? Select all that apply.
Choices (Students should refer to what is shown on eLC)
cd /home/users/user/exercise1/school/1302cd exercise1/school/1302cd 1302cd ~/1302cd ~/exercise1/school/1302cd /exercise1/school/1302
Solution
a, b, e
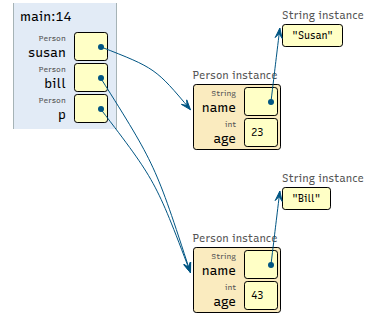
Memory Map: Person Class
Note
This question tests the students’ ability to understand code that declares multiple reference variables and objects. It also tests whether or not they understand that two variables can reference the same object.
The exercise is very similar to the book question in section 1.3 - Reference Type Examples.
Person Class
Consider the code for a Person class below, which is used
throughout this question.
1public class Person {
2
3 private String name;
4 private int age;
5
6 public Person(String name, int age) {
7 this.name = name;
8 this.age = age;
9 } // Person
10
11 public int getAge() {
12 return this.age;
13 } // getAge
14
15 public void setAge(int age) {
16 this.age = age;
17 } // setAge
18
19} // Person
Question 2
Draw a memory map diagram depicting the state of the variables after the first half of the code below executes. Once your memory map is complete, select the correct option below that matches the output from the last three lines of code (marked “second half”).
// first half
Person susan = new Person("Susan", 23);
Person bill = new Person("Bill", 22);
Person p = bill;
p.setAge(43);
// second half
System.out.println(susan.getAge());
System.out.println(bill.getAge());
System.out.println(p.getAge());
Choices (Students should refer to what is shown on eLC)
23 22 43
43 43 43
23 43 43
23 23 43
23 23 23
This code will not compile, so there will be no output.
Solution
c