2.2. Default Package¶
Prerequisite Content
This section assumes that the reader is familiar with the content of the “Executing Programs” video (Video #1 under “1301 Videos” on eLC). If you have not watched that video, please take a few minutes to do so now.
In this section, we will see how to compile a Java file using the default
package as a warm-up (i.e., we will compile a class in a package-less
.java file). This Java file will not be contained
within a named package. In the next section, we will see how to add the
file to a named package.
2.2.1. Setting up the Environment¶
Learn by Experimenting!
For each of the remaining sections in this chapter, be sure to login to Odin and type out the commands given in each part, taking notes as needed. When you are done, you will have a step-by-step outline for creating packages (both named and unnamed) in Java. Your notes and will be very useful on upcoming assignments and projects.
On Odin, complete each of the following steps:
From your home directory, create a directory for this tutorial called
cs1302-packagesand change into it using the following commands:cdmkdir cs1302-packagescd cs1302-packages
Use the
mkdircommand to create asrcdirectory and abindirectory withincs1302-packages. When you are done, you should have the following subdirectory structure for the source code and compiled code we will create shortly:cs1302-packages ├── bin └── src
Each directory above plays a role in the example. Here is a breakdown of the different subdirectories and their roles:
cs1302-packagesis the top-level assignment/tutorial directory. We create this folder so you have a place to organize all of the work you do in this tutorial. You will have similar directories for homeworks, projects, and other tutorials throughout the course.srcwill contain our.javafiles in this section. Since we are not (yet) compiling to a named package, we will place the files directly insrcwhich is known as the default (no-name) package for source code.binwill contain our.classfiles in this section. Since we are not (yet) compiling to a named package, we will place the files directly inbinwhich is known as the default (no-name) package for compiled code.
If you aren’t already in the
cs1302-packagesdirectory, change into it and run thetreecommand to make sure the directory contains all of the required subdirectories and that those subdirectories are organized correctly.
Short Video Demo of the Steps Above
Here is a short video demonstrating these steps in case you get stuck:
Test Yourself
You just ran tree inside the cs1302-packages directory and
see this output:
.
├── bin
└── src
Currently, there are no .java or .class files in the directory.
If we were to add them, which type of files would go in src and which
ones would go in bin?
Test Yourself Solution (Open after attempting the question above)
The .java file should be located in the src folder, and
the .class file should be inside the bin folder.
2.2.2. Creating a Program¶
Remember, the src directory you created in the previous section is
called the default package for source code. In this section, we
will place our source code directly in the default (no-name)
package. When developing small or temporary applications, it is a
convenient place for package-less .java files [2].
Let’s dive in!
From within the
cs1302-packagesdirectory you created in the previous section, create and open file in thesrcdirectory calledHelloWorld.javausing the following command:emacs src/HelloWorld.javaNote the relative path used in the above command. Because we used
src/HelloWorld.java, theHelloWorld.javafile will be placed within thesrcdirectory (the default package for source code).You should be presented with a blank file in the Emacs editor. Now, create a basic “Hello, World!” program in that file. The class should be called
HelloWorldto match the file name. For example, the contents of theHelloWorld.javafile might be:public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello, World!"); } // main } // HelloWorld
2.2.3. Compiling the Program¶
We have already placed the source code in the default package for source code (
src). When we compile, we want the compiled.classfile to end up in the default package for compiled code (bin). This helps us keep the.javafiles separate from the.classfiles.Go ahead and exit Emacs and compile the
HelloWorld.javafile using the command below to run the Java compiler (javac):javac -d bin src/HelloWorld.java
Warning
If you are not in the
cs1302-packagesdirectory, then the command above will not work.Understanding the Command
-dstands for destination. The syntax is to put-dfollowed by the location where we want the resulting.classfiles to be placed (their destination).In English, the command above tells the Java compiler to: “compile the
HelloWorld.javafile located in thesrcfolder and place the resulting.classfile into thebinfolder. Note the use of relative paths in this command (binandsrc/HelloWorld.javaare relative to our current location.Run the
treecommand from withincs1302-packages. You should see that theHelloWorld.javafile is in thesrcfolder and that theHelloWorld.classfile is in thebinfolder. Now, that’s organized!
2.2.4. Running the Program¶
Now that the class is compiled, we should note a few important things before running the program:
The
javacommand requires the FQN of the class (not the name of the.classfile).Note
Since our
HelloWorldclass is not in a named package (we compiled to the default package), its FQN is the same as its simple class name,HelloWorld.When executing the
javacommand, Java looks in your current working directory for the.classfiles it needs to run. Since we are in thecs1302-packagesdirectory, it will not be able to find the.classfiles unless we tell it where to find them. For this reason, we need to specify the default package for compiled code (bin) using a command line option called-cpfor class path. As its name suggests, the class path is the path to the default package for compiled code.
Here is the command to run the program:
java -cp bin HelloWorld
Warning
If you are not in the
cs1302-packagesdirectory, then the command above will not work.Understanding the Command
In English, the command above tells Java to: “run the
HelloWorldclass located in the default package and check thebinfolder for the.classfile it needs.You can execute a Java program anywhere on the system as long as you know the fully qualified name of the class containing the
mainmethod and the location of that compiled class’s associated default package, assuming proper file permissions.Test Yourself
Change directories into your home directory and see if you can run
HelloWorld.classfrom that location. Note: The relative path you provide as part of the classpath-cpwill have to change. What about the FQN? Write the command you used in your notes.Test Yourself Solution (Open after attempting the question above)
Once you are in your home directory, the command to run
HelloWorldwill have to change. Specifically, you need to put the location of the default package for compiled code on the classpath (using a relative or absolute path). The FQN of the class does not change.java -cp cs1302-packages/bin HelloWorld
Warning
The command above assumes that you are currently in your home directory and that the
cs1302-packagesdirectory is directly inside your home directory. If one or neither of those assumptions is true, then the command will not work.Important
In the command above,
binis just the relative path to the directory where the compiled.classfiles will be placed. In our example,binis a directory located inside of the present working directory. You can replacebinwith any relative or absolute path to any directory that you have permission to write to. For example, if we had a directory calledclass_filesin our present working directory, we could compile the code with-d class_filesand our.classfiles would be placed in that directory.Pro Tip
When you’re first starting out in a Unix environment, you might feel lost at times. Remember, it’s always important to know your present working directory (pwd) as that is the location where the commands you enter will be run. In the commands above, our pwd is
cs1302-packages. Since theHelloWorld.javafile is not in that directory, we had to specify the relative pathsrc/HelloWorld.javato tell the compiler how to find that file relative to the pwd. We’re telling the compiler “first, go into thesrcdirectory, and then you’ll see the fileHelloWorld.java.We will use the Unix
treecommand (or the similarfind) often in this course to see all files in a directory and its subdirectories. Go ahead and executetreefrom within thecs1302-packagesdirectory. If you have followed the steps correctly up until now, you will see the following output: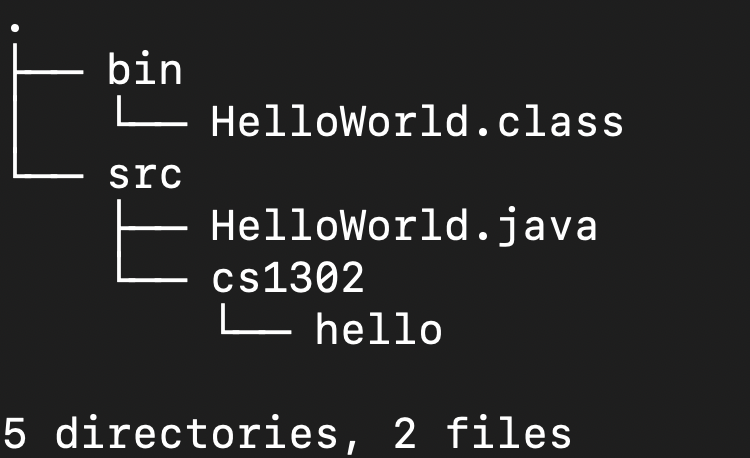
The output of the
treecommand shows that we successfully separated the source code (src) from the compiled code (bin). If you see any tilde (~) files, those are just backup copies of older versions of your files. You can ignore those.Let’s clean up! Delete the
HelloWorld.classfile that you created in thebinfolder (use thermcommand with a valid relative path to the file. Remember to use tab completion so you don’t have to type long filenames! In general, you don’t need to delete your.classfiles, but we will do so in this example because we will compile the code to a different directory in the next section.
Short Video Demo of the Steps Above
Here is a video outlining the steps in this section if you get stuck:
2.2.5. Final Considerations¶
Remember, source code should only be placed directly in
the default package directory (src) for convenience when
developing small or temporary applications or when just beginning
development
[2].
In the next section, we will see how to compile our files to a named package.